So lesen Sie die EDID Ihres Monitors mit einem Raspberry Pi

In diesem Beitrag erklären wir Ihnen genau, was Sie tun müssen, um die erweiterten Display-Identifikationsdaten (EDID) Ihres Monitors auf Ihrem Raspberry Pi zu nutzen.
Hinweis: Früher war eine Funktion zum Lesen der EDID in der Standalone-Version von PiDoctor verfügbar. Diese Version wurde eingestellt, und die Funktion zum Lesen der EDID ist in der neuen Version nicht mehr enthalten. PiCockpit PiDoctor App noch nicht, deshalb gebe ich Ihnen in diesem Artikel eine Anleitung, wie Sie die EDID lesen können.
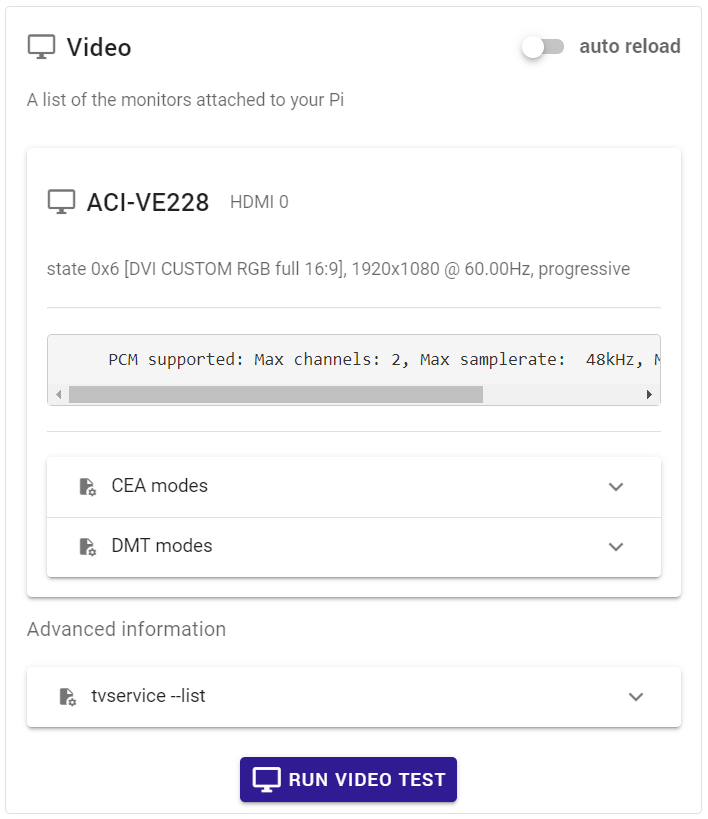
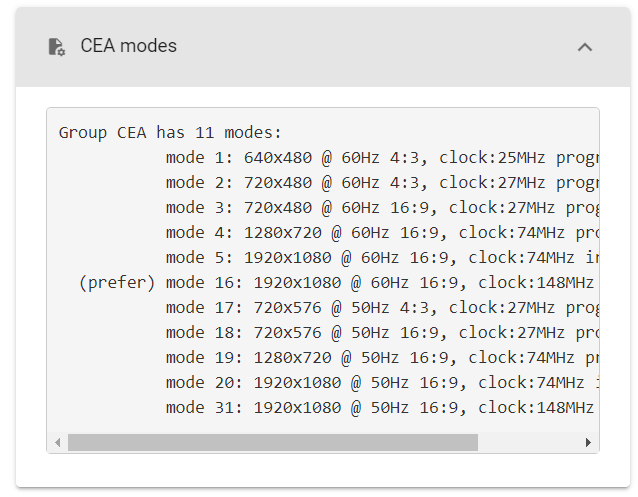
PiDoctor beinhaltet die Ausgabe auf dem Monitor
Bevor wir uns damit beschäftigen, wie Sie die EDID auf Ihrem Raspberry Pi extrahieren können, sollten Sie beachten, dass die neue PiCockpit's PiDoctor App enthält viele Ausgaben, die man beim Lesen der EDID erwarten würde (unterstützte Auflösungsmodi, Monitorname, Audiounterstützung, ...), hier sind zwei Beispiel-Screenshots:
Lesen Sie die EDID unter Raspbian / Raspberry Pi OS
Führen Sie den folgenden Befehl in der Befehlszeile aus:
tvservice -d /tmp/edid.dat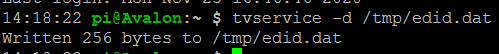
Dadurch wird die Datei edid.dat im Verzeichnis /tmp erstellt.
Hinweis: An einem Raspberry Pi 4 und 400 können zwei Displays über die microHDMI-Ports angeschlossen werden. In diesem Fall müssen Sie das Display angeben, von dem die EDID gelesen werden soll:
tvservice --list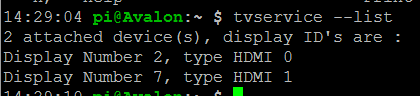
Geben Sie dann die Geräte-ID des Displays ein, an dem Sie interessiert sind, etwa so:
tvservice --device 2 -d /tmp/edid.datEDID mit edidparser dekodieren
Sie können edidparser auf diese Datei anwenden (wenn es nicht auf Ihrem System ist, installieren Sie es bitte zuerst):
edidparser /tmp/edid.datDadurch erhalten Sie eine Vielzahl von Ergebnissen, zum Beispiel auf meinem Monitor:
Enabling fuzzy format match…
Parsing /tmp/edid.dat…
HDMI:EDID version 1.3, 1 extensions, screen size 48x27 cm
HDMI:EDID features - videodef 0x80 standby suspend active off; colour encoding:RGB444|YCbCr422; sRGB is not default colourspace; preferred format is native; does not support GTF
HDMI:EDID found monitor range descriptor tag 0xfd
HDMI:EDID monitor range offsets: V min=0, V max=0, H min=0, H max=0
HDMI:EDID monitor range: vertical is 50-76 Hz, horizontal is 30-83 kHz, max pixel clock is 170 MHz
HDMI:EDID monitor range does not support GTF
HDMI:EDID found monitor name descriptor tag 0xfc
HDMI:EDID monitor name is VE228
HDMI:EDID found monitor S/N descriptor tag 0xff
HDMI:EDID found preferred CEA detail timing format: 1920x1080p @ 60 Hz (16)
HDMI:EDID established timing I/II bytes are BF EF 00
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 4, 640x480p @ 60 Hz in established timing I/II
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 5, 640x480p @ 72 Hz in established timing I/II
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 6, 640x480p @ 75 Hz in established timing I/II
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 8, 800x600p @ 56 Hz in established timing I/II
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 9, 800x600p @ 60 Hz in established timing I/II
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 10, 800x600p @ 72 Hz in established timing I/II
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 11, 800x600p @ 75 Hz in established timing I/II
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 16, 1024x768p @ 60 Hz in established timing I/II
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 17, 1024x768p @ 70 Hz in established timing I/II
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 18, 1024x768p @ 75 Hz in established timing I/II
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 36, 1280x1024p @ 75 Hz in established timing I/II
HDMI:EDID standard timings block x 8: 0x714F 8180 8140 9500 A940 B300 D1C0 0101
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 21, 1152x864p @ 75 Hz (4:3) in standard timing 0
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 35, 1280x1024p @ 60 Hz (5:4) in standard timing 1
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 32, 1280x960p @ 60 Hz (4:3) in standard timing 2
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 47, 1440x900p @ 60 Hz (16:10) in standard timing 3
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 51, 1600x1200p @ 60 Hz (4:3) in standard timing 4
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 58, 1680x1050p @ 60 Hz (16:10) in standard timing 5
HDMI:EDID found DMT format: code 82, 1920x1080p @ 60 Hz (16:9) in standard timing 6
HDMI:EDID parsing v3 CEA extension 0
HDMI:EDID monitor support - underscan IT formats:yes, basic audio:yes, yuv444:yes, yuv422:yes, #native DTD:1
HDMI:EDID failed to find a matching detail format for 1920x1080p hfp:48 hs:32 hbp:80 vfp:3 vs:5 vbp:22 pixel clock:138 MHz
HDMI:EDID calculated refresh rate is 60 Hz
HDMI:EDID guessing the format to be 1920x1080p @60 Hz
HDMI:EDID found CEA detail timing format: 1920x1080p @ 60 Hz (16)
HDMI:EDID found DMT detail timing format: 1366x768p @ 60 Hz (81)
HDMI:EDID found CEA detail timing format: 1280x720p @ 60 Hz (4)
HDMI:EDID found CEA detail timing format: 720x480p @ 60 Hz (2)
HDMI:EDID found CEA detail timing format: 1920x1080i @ 60 Hz (5)
HDMI:EDID found CEA format: code 16, 1920x1080p @ 60Hz (native)
HDMI:EDID found CEA format: code 5, 1920x1080i @ 60Hz
HDMI:EDID found CEA format: code 4, 1280x720p @ 60Hz
HDMI:EDID found CEA format: code 3, 720x480p @ 60Hz
HDMI:EDID found CEA format: code 2, 720x480p @ 60Hz
HDMI:EDID found CEA format: code 1, 640x480p @ 60Hz
HDMI:EDID found CEA format: code 17, 720x576p @ 50Hz
HDMI:EDID found CEA format: code 18, 720x576p @ 50Hz
HDMI:EDID found CEA format: code 19, 1280x720p @ 50Hz
HDMI:EDID found CEA format: code 20, 1920x1080i @ 50Hz
HDMI:EDID found CEA format: code 31, 1920x1080p @ 50Hz
HDMI:EDID found audio format 2 channels PCM, sample rate: 32|44|48 kHz, sample size: 16|20|24 bits
HDMI:EDID found HDMI VSDB length 5
HDMI:EDID HDMI VSDB has physical address 1.0.0.0
HDMI:EDID HDMI VSDB has no extension fields
HDMI:EDID filtering formats with pixel clock unlimited MHz or h. blanking unlimited
HDMI:EDID best score mode initialised to CEA (1) 640x480p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 25 MHz (score 0)
HDMI:EDID best score mode is now CEA (1) 640x480p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 25 MHz (score 61864)
HDMI:EDID best score mode is now CEA (2) 720x480p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 27 MHz (score 3066472)
HDMI:EDID CEA mode (3) 720x480p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 27 MHz has a score of 66472
HDMI:EDID best score mode is now CEA (4) 1280x720p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 74 MHz (score 3635592)
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (4) 640x480p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 25 MHz has a score of 18432
HDMI:EDID CEA mode (5) 1920x1080i @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 74 MHz has a score of 2773832
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (5) 640x480p @ 72 Hz with pixel clock 31 MHz has a score of 5529
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (6) 640x480p @ 75 Hz with pixel clock 31 MHz has a score of 5760
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (8) 800x600p @ 56 Hz with pixel clock 36 MHz has a score of 26880
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (9) 800x600p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 40 MHz has a score of 28800
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (10) 800x600p @ 72 Hz with pixel clock 50 MHz has a score of 8640
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (11) 800x600p @ 75 Hz with pixel clock 49 MHz has a score of 9000
HDMI:EDID best score mode is now CEA (16) 1920x1080p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 148 MHz (score 5398248)
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (16) 1024x768p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 65 MHz has a score of 47185
HDMI:EDID CEA mode (17) 720x576p @ 50 Hz with pixel clock 27 MHz has a score of 66472
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (17) 1024x768p @ 70 Hz with pixel clock 75 MHz has a score of 13762
HDMI:EDID CEA mode (18) 720x576p @ 50 Hz with pixel clock 27 MHz has a score of 66472
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (18) 1024x768p @ 75 Hz with pixel clock 78 MHz has a score of 14745
HDMI:EDID CEA mode (19) 1280x720p @ 50 Hz with pixel clock 74 MHz has a score of 117160
HDMI:EDID CEA mode (20) 1920x1080i @ 50 Hz with pixel clock 74 MHz has a score of 128680
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (21) 1152x864p @ 75 Hz with pixel clock 108 MHz has a score of 43662
HDMI:EDID CEA mode (31) 1920x1080p @ 50 Hz with pixel clock 148 MHz has a score of 232360
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (32) 1280x960p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 108 MHz has a score of 98728
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (35) 1280x1024p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 108 MHz has a score of 103643
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (36) 1280x1024p @ 75 Hz with pixel clock 135 MHz has a score of 24576
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (47) 1440x900p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 106 MHz has a score of 102760
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (51) 1600x1200p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 162 MHz has a score of 140200
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (58) 1680x1050p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 146 MHz has a score of 130840
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (81) 1366x768p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 85 MHz has a score of 4062945
HDMI:EDID DMT mode (82) 1920x1080p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 148 MHz has a score of 149416
HDMI0:EDID preferred mode remained as CEA (16) 1920x1080p @ 60 Hz with pixel clock 148 MHz
HDMI:EDID has HDMI support and audio support
edidparser exited with code 0Online-Decoder-Tool
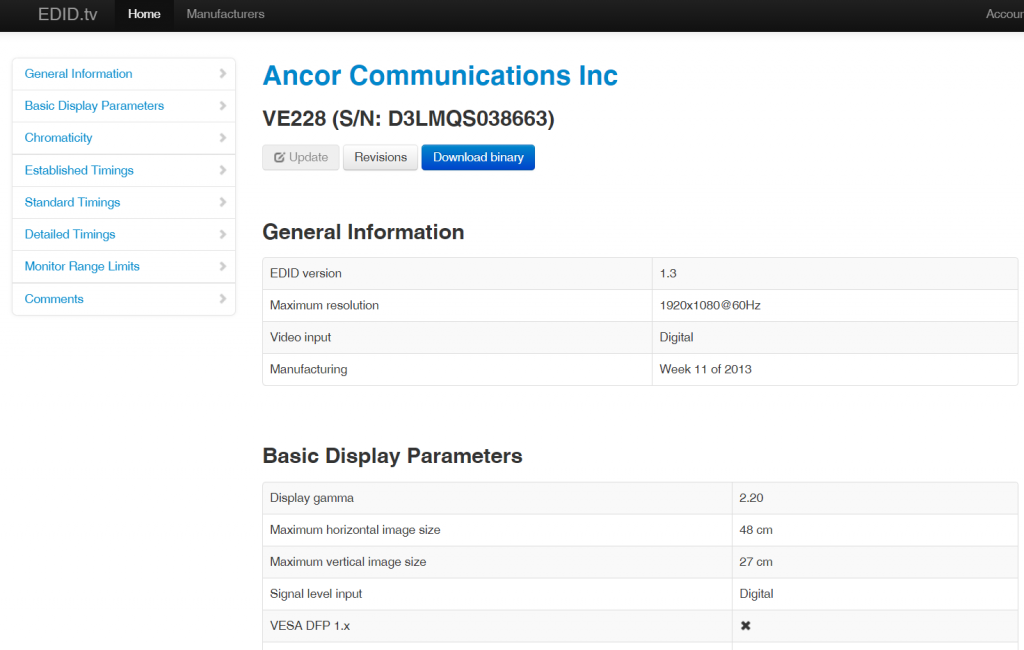
Sie können diese Datei auch in ein Online-Decoder-Tool hochladen, zum Beispiel edid.tv
Hinweis: In meinem Test beschwerte sich edid.tv über eine falsche Prüfsumme für eine meiner EDIDs - mir ist derzeit kein Workaround dafür bekannt.
Fehlersuche tvservice / EDID-Dump
Nichts geschrieben
Wenn ich laufe
tvservice -device 2 -d tmp/edid.datIch bekomme "Nichts geschrieben!"
Versuchen Sie nun, Folgendes zu überprüfen:
- ist Ihr Monitor an den HDMI-Anschluss angeschlossen (nein, im Ernst)
- Ist die Geräte-ID korrekt? Bitte verwenden Sie tvservice -liste um eine Liste der IDs zu erhalten, kopieren Sie nicht einfach mein Beispielgerät id 2
- Versuchen Sie tvservice ohne -Gerät 2
- Versuchen Sie, den Raspberry Pi neu zu starten (in diesem speziellen Anwendungsfall gibt es Probleme, wenn Monitore im laufenden Betrieb angeschlossen werden, AFAIK), und führen Sie die Befehle erneut aus.
- die anderen tvservice-Parameter ausprobieren, um zu überprüfen, ob eine Ausgabe von diesem bestimmten Monitor möglich ist (hier ist eine Dokumentation für tvservice)
- einige Fernseher/Monitore sind defekt und können keine EDID bereitstellen - versuchen Sie einen anderen Monitor, um zu sehen, ob es einen Unterschied macht
Schlussfolgerung
Jetzt, wo die erweiterten Identifikationsdaten Ihres Monitors endlich einen Sinn ergeben, können Sie mit Ihrem nächsten Raspberry Pi-Projekt beginnen!
Suchen Sie nach Ideen? Schauen Sie sich unsere Reihe Paragon-Projekte.
Bonjour, j'obtiens cette erreur :
tvservice wird bei Verwendung des Treibers vc4-kms-v3d nicht unterstützt.
Ähnliche Funktionen sind mit Standard-Linux-Tools verfügbar
wie z.B. modetest aus libdrm-tests.
Gibt es eine Alternative?
Vielen Dank,
Hallo Yoann, ich hatte dieses Problem auf dem Pi Zero 2, und vielleicht würde diese Lösung für Sie funktionieren: https://picockpit.com/raspberry-pi/the-big-raspberry-pi-zero-2-w-troubleshooting-guide/#Command_tvservice_throws_error